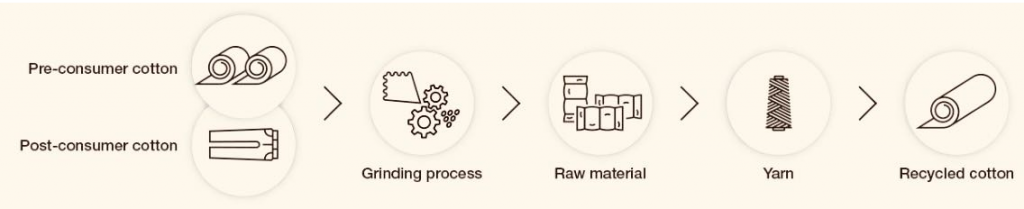
What is Recycled Cotton?
Recycled cotton is also commonly referred to as reclaimed cotton, or regenerated cotton, which can be generally defined as converting cotton fabric into cotton fiber that can be reused in textile products. Textile recycling is generated universally from two primary sources:
- Pre-consumer: includes scraps created by yarn and fabric by-products;
- Post-consumer: includes garments, upholstery, towels, household items to berepurposed.

Large-scale source of recycled cotton is produced from pre-consumer waste, such as cutting. Post-consumer waste is more difficult to sort due to shades of color, fabric blends, etc., and is often a labor-intensive process.
How is recycled cotton made?
Generally, recycled cotton yarn is scraps produced by yarn and fabric by-products or semi-finished products in the textile production process, as well as the scraps and leftovers produced in the cutting process of clothing, and discarded ones in daily activities, which are collected centrally, then proceed opening and scutching, removing impurities, dedusting, mixing, carding, drawing, and twist the yarn.
Firstly, “Flowering”:
Mainly defibrate the collected fabrics and materials, which are sorted into similar colours, then run through a machine that tear the large pieces of tangled fibers making them loose into small pieces or bundles, and at the same time, the loosening process is accompanied by mixing and impurity removal. After the flowering process, the fabrics and materials are processed into recycled cotton and packaged to provide raw materials for the production of recycled cotton yarn.
Secondly, Blowing and Carding:
The opening and cleaning process is the first process in the spinning process.
(1) Opening and Scutching: Through the tearing and blowing action of the cotton cleaning machine, the compressed block fibers in the cotton bale are loosened into small cotton bundles weighing 0.3-0.5g, which are Impurity removal and mixing create conditions for separation into single fibers.
(2) Impurity removal: while opening and scutching, remove impurities in the recycled cotton.
(3) Mixing: According to the requirements of the yarn, fully mix various raw materials (cotton fibers; chemical fibers) according to the proportion of cotton. The better the cotton is opened, the more uniform the mixing will be.
(4) Carding: the mixed cotton fiber, the output cotton flows to the cotton storage box of each carding machine in the carding process to form sliver for the drawing process.
Thirdly, Drawing frame:
Because the quality and structural state of the sliver are still far from the requirements of the final yarn, the straightness and separation of the fibers are poor. Therefore, the carded sliver needs to be carded before further spinning and combined to improve evenness and fiber state, the sliver made by the drawing frame is placed in a regular circle in the sliver can for transportation and storage for use in the next process.
Fourthly. Yarn forming:
The cotton sliver produced by drawing frame is used to condense and twist the fibers in the high-speed spinning rotor and output into yarn.
“ Shreds the fabric into yarns and produces recycled raw fibre that are spun back into yarns” –
The recycling process of shredding the fabric into its cruder forms is quite stressful and harsh. Fribers to break and entangle is a common phenomenon . This compromises the quality of the new fibre, making it shorter and harder to spin. The quality of recycled fiber will never have quality values equal to the original fiber. Specifically, fiber length and length uniformity will be impacted. Consequently, the new fibres are blended with other virgin materials, such as plastic or cotton, to improve strength and make them suitable for reuse.
Recycled cotton yarn features

High-quality recycled fibre with high breaking strength, which is generally more than 40 higher than that of cotton thread of the same specification;
Good wear resistance, generally 1 times higher than cotton threads of the same specification;
The shrinkage rate is small,which is only about 0.5
Natural material, it is suitable for sewing chemical fiber fabrics and anti-wrinkle high-cotton fabrics, and the stitches are flat and straight;
Good heat resistance, suitable for high-speed sewing machines of 3000-4000r/min, and ironing temperature around 160℃;
Good flexibility and elasticity, suitable for sewing high chemical fiber fabrics.
Recycled cotton fabric properties

Recycled cotton is a washable, easy to clean, and high-quality fabric. It’s has been used for many years as it offers numerous advantages for the fashion industry.
Recycled cotton fabrics look and feel like regular cotton. They are durable, lightweight, breathable, absorbent, and quick-drying.
Recycled cotton fabrics regulate body temperature very well and are perfect in hot weather. They keep the body cool and fresh and are therefore ideal for people with skin sensitivity.
You can easily print or screen-print recycled cotton. Dying is also effortless, fast, and long-lasting. Recycled cotton fabrics are available in a variety of colors.
Cotton recycling is an ecological textile production method. It conserves resources, reduces waste, and doesn’t involve harmful substances. The process significantly saves water, energy, and carbon dioxide emissions.
The regenerated material is also natural, bio-based, biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable. Recycled cotton is a great sustainable option, but its availability is limited.
What is Benefits & Challenges to Recycled Cotton Fiber

Benefits
Many different low-end products such as insulation, mop heads, rags, and stuffing can give a new life to Recycled Cotton. Due to the main advantage of cotton fiber is spinnability. The natural twist makes the cotton fiber have a certain amount of strength, which is beneficial to the spinning process.
According to the relevant news report, annual textile waste is estimated to 26 million tons (only China). The process of recycling allows the item to find a new purpose as something else, diverting many products from landfills and incinerators and help the fashion industry to be less wasteful.
As we all know, cotton as primary choice of fabric for textile industry. However, cotton production is environmentally dependent, especially on water supplies. Besides of that, the use of polluting pesticides and chemicals to protect crops and land clearance also are issues caused by cotton production.Therefore, As there is no need for dyeing, regenerated cotton helps to reduce water, chemical and energy consumption, i.e. recycling reduces the loss of ecological resources to a certain extent.
There is no static electricity, good moisture absorption and perspiration, good air permeability, and is relatively close to the human body. The clothing made of it is comfortable to wear, has no pilling phenomenon, and feels soft. Alkali and acid resistance, excellent alkali resistance. The strength of cotton fibers will increase by 10% in the state of humidity. Cotton has excellent dyeing properties and is easy to dye. Recycled Cotton not only keep the features of regular cotton to some extent, but also make the end-use application more environment-friendly.
Challenges
During recycling, the salvaged cotton fibers and scraps weaken. Therefore, the amount of recycled cotton in an item will eventually harm the product’s yarn and fabric properties such as strength, length, strength, uniformity, texture, and evenness, among others.
The risk of contamination by other fibers is much higher for recycled cotton than other recycled fibers. Stitching and sewing threads of different materials as well as small amounts of spandex are likely to be present in the final composition, especially if the garments it comes from were not designed to be recycled following Eco-Design rules.
Cotton must be blended with other fibers to be made into new yarn for strength and durability, and therefore cannot continuously be recycled.
Whatever is produced with it, recycled cotton garment cannot be recycled again, as the fibers are already weakened a lot during the first recycling process.
Even though Recycled cotton is also known as upcycled cotton and made from post-consumer or post-industrial cotton waste. Unfortunately, it remains cost-prohibitive due to high production costs and limited availability.
Which certificates exist?
Many of the best certification standards for textiles apply to recycled cotton. It’s a natural fabric and considered one of the most environmentally-friendly textile products.
Fashion brands and retailers often source recycled cotton sustainability from manufacturers carrying some of the following certifications:
Global Recycled Standard (GRS) – is a voluntary product standard for tracking and verifying the content of recycled materials in a final product. The standard applies to the full supply chain and addresses traceability, environmental principles, social requirements, chemical content and labeling.
Global Organic Textile Standards (GOTS) – is an internationally recognised organic textile standard, which ensures the organic status of textiles from the harvesting of the raw materials through environmentally and socially responsible manufacturing all the way to labelling, in order to provide credible assurances to the consumer.
Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) – is a non-profit international membership organization. Committed to improving cotton planting methods, promoting the sustainable development of the cotton industry, and making Better Cotton a mainstream sustainable commodity on a global scale. Track the movement of Better Cotton through the supply chain by certifying cotton grower units and implementing supply chain monitoring documents.

Can recycled cotton(regenerated cotton) replace virgin cotton?
According to the actual cotton source, it is divided into virgin cotton fabric and recycled cotton fabric.
Pure cotton is a natural fiber with good hygroscopicity, moisture retention, heat resistance, alkali resistance and hygiene. However, pure cotton fabrics are easy to wrinkle, and they are difficult to smooth after wrinkling; they are easy to shrink, and the shrinkage rate of pure cotton clothes is 2% to 5%. Deformation, especially in summer clothes, because the fabric is thin; easy to stick hair, difficult to completely remove.
While for recycled cotton(regenerated cotton), after a harsh mechanical recycling process, recycled fibre deteriorates in quality. As a result, most regenerated cotton is ‘downcycled’ to lower quality products like insulation, mop heads and padding. To use regenerated cotton for higher-end use like fashion, it must blend with other fibres to achieve good strength and durability. For instance, canvas contains 65% regenerated cotton and 35% virgin cotton. Once blended, fibres cannot be recycled again because of the difficulty to separate the different fibres.
How to promote recycled cotton

With increasing consumer focus on sustainability and circularity, recycled textiles are seen by many as a key driver toward more sustainable apparel, which meanwhile is a great method to keep your clothes out of landfills. Due to its natural fiber properties, cotton has a unique opportunity in the sector of recycled apparel.
Companies should consider using virgin cotton and promote its sustainable natural benefits. Further moving away from a linear economy (make, use, dispose) to a circular economy; moving toward a greater need for improving the life of garments rather than promoting a disposable business model. Even though there are still challenges need to be overcomed for end-uses, but Recycled Cotton is still a great option for reducing textile waste and repurposing for part of products.
As consumers, there are a number of approaches that can be taken to reduce the amount of cotton used in our lives. One is simply buying fewer, better quality clothes and cotton products, buying second-hand, or repurposing. Another is participating in textile recycling programs, such as donate old clothing that’s in good condition. A third is buying items made from recycled cotton without the use of harmful chemicals or pesticides. Any methods you choose, only by discarding your used clothes responsibly, can you do your part to protect the environment.


